What Are Collagen Peptides?
Collagen peptides represent a highly functional protein source, central to balanced nutrition and overall well-being. Their unique nutritional and physiological characteristics support bone and joint health while also enhancing skin appearance.
Collagen itself is composed of three polypeptide α-chains, intricately entwined to form triple-helical macromolecules. This distinctive structure, defined by its size and amino acid composition, is characterized by glycine occupying every third position in the sequence—enabling the formation of the triple helix. The repeating sequence (Gly-X-Y)*n, where X and Y are often proline and hydroxyproline, is essential for collagen’s assembly into fibrils. These fibrils subsequently create fibers that deliver exceptional structural stability to the extracellular matrix within connective tissues.
Defining Collagen Peptides
The foundation for both gelatin and collagen peptides is collagen protein. Collagen peptides are distinguished by their relatively low molecular weight—less than 10,000 g/mol—and consist of between two and one hundred amino acids. Their superior solubility in cold water and their non-gelling properties, even at high concentrations, make them highly versatile for a range of applications.
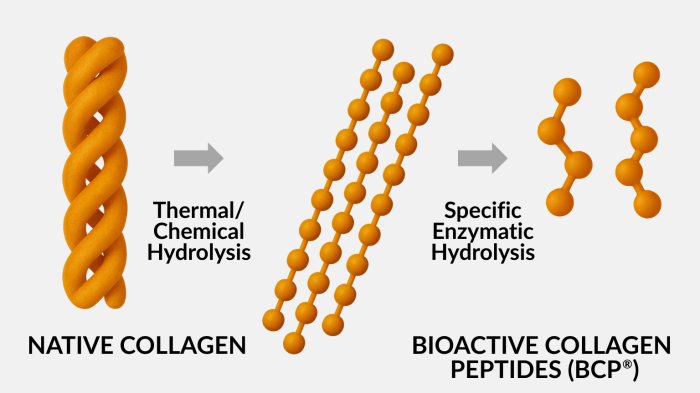
Production Process: From Native Collagen to Bioactive Peptides
At GELITA, collagen peptides are produced through precisely controlled enzymatic hydrolysis of collagen sourced from bovine hide, bone, pigskin, or fish. The process involves extraction, enzymatic hydrolysis, purification, concentration, sterilization, and drying. This rigorous methodology ensures exceptional product safety, as validated by numerous international studies.
The production is meticulously optimized to yield peptides with targeted functionalities. During processing, the triple helix structure is disrupted; long chains are hydrolyzed into shorter fragments, some of which possess bioactive properties that stimulate specific biological responses.
Sourced From Nature
Our collagen peptides originate from natural animal-derived raw materials that have been inspected and approved for human consumption by veterinary authorities. Collagen protein—abundant in skin and bone—serves as the primary raw material. Our suppliers within the meat processing industry provide these materials fresh, cooled, or deep-frozen based on logistical requirements. If necessary, they are stored in our temperature-controlled facilities until further processing.
Experience the Benefits of Bioactive Collagen Peptides
With scientifically validated processes and a commitment to delivering premium quality, GELITA’s collagen peptides empower product development teams, R&D professionals, and quality assurance experts to create innovative solutions that elevate health and sensory experiences across global markets.
Now ready to take your formulations to the next level?
Get in touch with our experts to unlock the full potential of Bioactive Collagen Peptides for your products.