And Where Does It Come From?
Gelatin is a natural, high-purity protein derived from collagen, which is abundantly found in animal connective tissue. It is produced using raw materials approved for human consumption and meets the highest food safety standards. Extracted from pigskins, bovine hides, and demineralized bones, gelatin can also be obtained from other species — particularly chicken and fish — to meet specific dietary, cultural, or religious requirements.
- Raw materials are certified by veterinary authorities
- Collagen is the essential protein for gelatin production
What Makes Collagen Unique as a Protein Source?
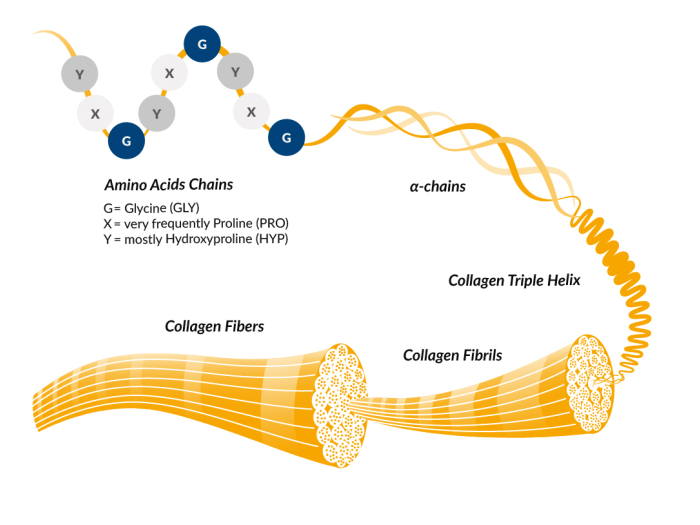
Collagen is the primary structural protein in humans and animals, forming the foundation of skin, bones, and connective tissue. Its unique triple helix structure makes it ideal for gelatin production.
- Composed of ~1,050 amino acids per chain
- Three chains form a triple helix, creating collagen fibrils
- High in hydroxyproline—unlike most other proteins
- Characteristic motifs: glycine-proline-X and glycine-X-hydroxyproline
How Is Gelatin Made?
Step 1: Pretreatment
Preparing the Raw Materials
Before processing, raw materials are thoroughly cleaned and conditioned to allow for effective extraction.
- Gelatin Type A (acid process): 24-hour acid conditioning (primarily pigskin)
- Gelatin Type B (alkaline process): Long-term alkali treatment of bovine hides or ossein. Enables the collagen structure to be gently transformed
Step 2: Extraction
Isolating the Gelatin
Gelatin is extracted using warm water in multiple stages, each tailored for optimal yield and quality.
- Initial extraction at lower temperatures yields firmer gelatin
- Repeated extractions at higher temperatures complete the process
- Continuous process option: enables real-time gelatin production with adjustable parameters
Step 3: Purification
Ensuring Cleanliness and Purity
The gelatin solution is purified using industry-grade techniques to remove all insoluble and unwanted substances.
- High-performance separators remove fat and solids
- Diatomaceous earth (Kieselgur) and cellulose filters trap fine particles
- Ion exchange purification eliminates residual salts
Step 4: Concentration
Creating a Stable Gelatin Solution
Water is gently removed under vacuum conditions, resulting in a concentrated, syrup-like viscous solution.
- Multi-stage evaporators preserve protein structure
- Final filtration ensures clarity and quality
Step 5: Drying
Forming Gelatin Noodles
Sterilized and cooled, the gelatin sets into dry, brittle noodles before further processing.
- Dried with sterile, filtered air
- Broken down and milled after drying
- Every batch undergoes strict lab testing before release
Step 6: Milling, Sieving & Blending
Tailoring to Customer Needs
The final dried gelatin is customized according to application-specific requirements.
- Granulated, sieved, and blended to specification
- Packed into silos or bags
- Shipped only after receiving final laboratory clearance
Are the Raw Materials Safe for Human Use?
Yes. GELITA exclusively sources its gelatin from collagen-rich materials that are certified safe for human consumption.
- Based on safe, compliant raw materials monitored throughout the production process
- Materials delivered fresh, chilled, or deep-frozen
- Stored under strict refrigeration when not immediately processed
How Does GELITA Ensure Quality and Safety?
Our certified production systems are designed to meet the strictest international food and environmental standards.Interested in High-Performance Gelatin Solutions?
Whether you're in pharmaceuticals, food manufacturing, or health and nutrition, GELITA offers industry-leading gelatin solutions with full quality assurance and regulatory compliance.
Learn more about our production standards, application support, or tailored gelatin specifications.